Instrument Description





Next: Apertures: entrance optics
Up: Observer's Manual
Previous: SWS Observing Time
The SWS instrument consists of two nearly independent grating spectrometers,
together covering the wavelength range 2.38-45.2 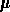 m with an overall
spectral resolution of
m with an overall
spectral resolution of 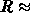 1,000-2,000 (i.e.,
1,000-2,000 (i.e., 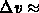 300-150
km s
300-150
km s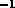 ). By inserting Fabry-Pérot (F-P) filters, one for the range
15-26
). By inserting Fabry-Pérot (F-P) filters, one for the range
15-26 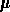 m (with capability down to 11.4
m (with capability down to 11.4 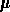 m at reduced
resolution) and the other for the region
26-35
m at reduced
resolution) and the other for the region
26-35 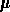 m (with capability to 44.5
m (with capability to 44.5 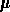 m at reduced sensitivity), the
resolution can be increased to
m at reduced sensitivity), the
resolution can be increased to 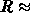 30,000 (i.e.,
30,000 (i.e., 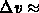 10
km s
10
km s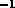 ) .
) .
 N.B.: Click here for better view
N.B.: Click here for better view
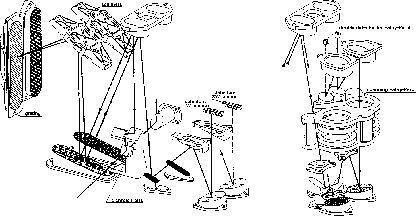
Figure: Lay-out of SWS
Fig.  gives an impression of the lay-out of the SWS,
an optical block diagram is shown in
Fig.
gives an impression of the lay-out of the SWS,
an optical block diagram is shown in
Fig.  , and an optical schematic is shown in
Fig.
, and an optical schematic is shown in
Fig.  .
The IR radiation is reflected into the SWS by the ISO pyramidal mirror.
The SWS has three entrance apertures , each with its
own dichroic beamsplitter feeding the Short Wavelength section and the Long
Wavelength section. The appropriate entrance aperture will be selected
by specific pointing of the ISO satellite. A four-position selection
mechanism permits opening of any one of these apertures or blocking of
all three.
.
The IR radiation is reflected into the SWS by the ISO pyramidal mirror.
The SWS has three entrance apertures , each with its
own dichroic beamsplitter feeding the Short Wavelength section and the Long
Wavelength section. The appropriate entrance aperture will be selected
by specific pointing of the ISO satellite. A four-position selection
mechanism permits opening of any one of these apertures or blocking of
all three.
Tab.  shows how the SWS grating wavelength region is subdivided in
16 wavelength bands , instrumentally dictated
by aperture , spectral order, filter material and
detector type.
shows how the SWS grating wavelength region is subdivided in
16 wavelength bands , instrumentally dictated
by aperture , spectral order, filter material and
detector type.
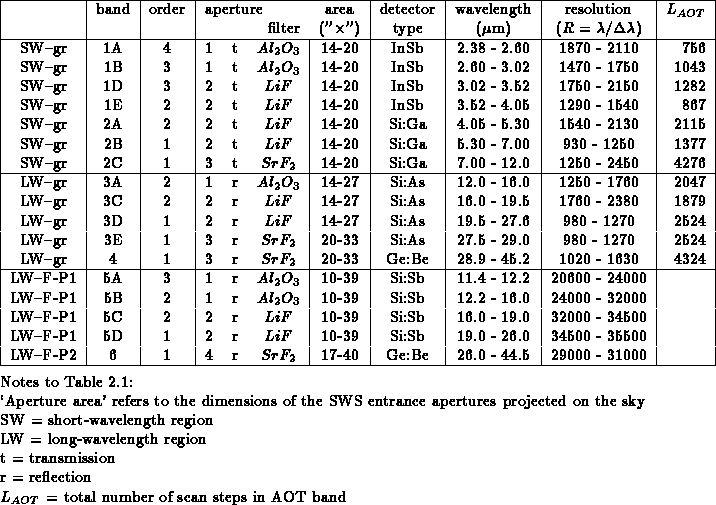
Table: Definition of the wavelength ranges of the SWS AOT bands
SWS Consortium
Tue Jul 30 15:56:20 MET DST 1996
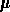 m with an overall
spectral resolution of
m with an overall
spectral resolution of 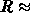 1,000-2,000 (i.e.,
1,000-2,000 (i.e., 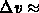 300-150
km s
300-150
km s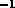 ). By inserting Fabry-Pérot (F-P) filters, one for the range
15-26
). By inserting Fabry-Pérot (F-P) filters, one for the range
15-26 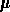 m (with capability down to 11.4
m (with capability down to 11.4 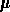 m at reduced
resolution) and the other for the region
26-35
m at reduced
resolution) and the other for the region
26-35 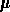 m (with capability to 44.5
m (with capability to 44.5 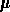 m at reduced sensitivity), the
resolution can be increased to
m at reduced sensitivity), the
resolution can be increased to 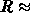 30,000 (i.e.,
30,000 (i.e., 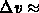 10
km s
10
km s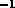 ) .
) .








