AKARI Q&A
- What is ASTRO-F?
- What is infrared light? What can you see through the infrared light?
- What sort of satellite was AKARI?
- Why did AKARI go to space?
- What did AKARI perform in space?
- What did you study by AKARI?
- Who made AKARI?
- What is ASTRO-F?
-
ASTRO-F is an astronomical satellite to observe the Universe in the infrared light. The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science and collaborators developed it. The ASTRO-F was given a nickname of "AKARI" after the launch. "AKARI" means a "light" in Japanese.
- What is infrared light? What can you see through the infrared light?
-
Infrared light is an invisible light with a longer wavelength than normal visible light.
As a rainbow can be divided into some colours, there are several kinds of infrared light. They are called near-infrared, mid-infrared, and far-infrared in order of distance from red colour in a rainbow. When you look into the Universe in an appropriate infrared light, you can see a star and a galaxy beyond an opaque dust cloud, or you can see the dust cloud (temperature of less than -200℃) itself.
You can observe an aspect of the Universe which cannot be seen with visible light, and investigate the mysteries of the birth, death, and evolution of stars and galaxies.

The human eye can see the several colours of the rainbow, but there are other invisible lights outside them. The infrared light is next to the red of the rainbow. 
The Milky Way seen at various wavelengths of light (photo by NASA). There are black belts which are the areas hidden by dust clouds, when you see it with visible light (bottom). Many stars can be seen through the clouds when you see with near-infrared light (middle). Stars disappear but dust clouds radiate brightly at far-infrared wavelengths (top).
- What sort of satellite was AKARI?
-
AKARI had a height of 3.7 m and a weight of 950 kg (at launch time). It was equipped with a telescope of 68.5 cm primary mirror and two sets of instruments for infrared observations.
The entire telescope and observation instruments were cooled down to around -270℃ in order to detect faint infrared rays from the distant Universe.

AKARI assembled temporally for tests. Telescope and observation instruments were inside the upper cylinder (a cryostat) and cooled down to around -270℃. The lower (golden) part is called the bus module. It controlled the entire satellite.
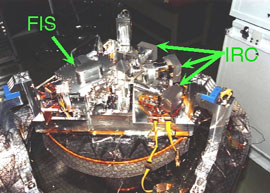
Scientific instruments of AKARI. The FIS is for far-infrared and the IRC is for near- and mid-infrared. 
The telescope of 68.5 cm diameter. The surface was coated with gold so as to reflect infrared rays efficiently.
- Why did AKARI go to space?
-
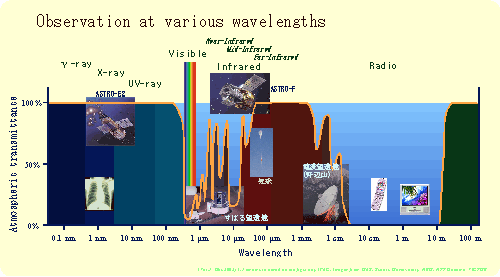
Most of the infrared light do not reach the ground due to absorption by the atmosphere. AKARI was a satellite for thorough studies in the infrared which cannot be made from the ground.
- What did AKARI perform in space?
-

IRAS satellite which was launched by the U.S., U.K., and the Netherlands in 1983 made a infrared map of the Universe. AKARI made observations in a similar way and investigated the more distant Universe. AKARI made catalogues of infrared objects by observing all over the sky. The catalogues have been published for the benefit of astronomers in the world and have been used for astronomical studies by them.
AKARI made detailed observations toward selected regions as well as an all-sky (survey) observation.
- What did you study by AKARI?
-
The catalogue made by AKARI includes approximately million objects. Astronomers can research how stars and galaxies are born and grow with the catalogue statistically. In addition to these studies, AKARI observational data are used by astronomers around the world for many purposes.
Selected objects requested by astronomers varied greatly. For example, very distant newborn galaxies, neighbour galaxies, nascent stars, stars which are forming planets, stars near its life's end, or asteroids.
- Who made AKARI?
-

AKARI had been developed by the Institute of the Space and Astronautical Science in collaboration with members in universities and other institutes. Korean and European members had also joined the AKARI project. Of course, many companies contributed to the development of the satellite and instruments.





